By Anjaneyulu Nambi, Head SOC Operations, Alliant Cybersecurity
It is a well-documented fact that small businesses are targeted most often by cyberattacks. In fact, according to a recent Senate Judiciary Hearing, three out of four cybersecurity incidents in the US were targeted at small businesses. The Senators also pointed out that malicious actors do not always target companies with deep pockets. Further, most small businesses have already been pushed to the brink due to the pandemic. However, what was most worrisome was that 51 percent of companies do not have any cybersecurity resources in place.
The threat landscape for small to medium-sized businesses (SMB) is numerous and include the following:
- Email;
- Mobile devices;
- Corporate website;
- Social media;
- Ecommerce systems;
- Online banking;
- BYOD and office policy;
- Network management; and
- Backup and remote access.
Small Business, Big Impact
Cyberattacks on SMBs have a significant impact. In fact, 60 percent of small companies go out of business within six months of falling victim to a data breach or cyberattack. Let us briefly look at the impact cyberattacks can have on businesses.
- Vulnerability: Attackers can see small businesses as easy targets;
- Business Costs: Cyberattacks often takes a huge toll on businesses and threaten the viability of the organization; and
- Reputation: Customers and employees expect and trust you to keep their information secure.
The cybersecurity threats that most businesses face include the following:
- Phishing Attacks;
- Ransomware;
- Hacking;
- Imposter Scams; and
- Environmental Events.
SMB Cyber-Security Spending Worldwide: Trends and Forecasts Overview 2020–2025
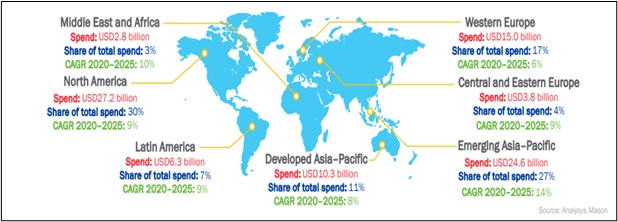
Before the pandemic, cyber-crime was already weighing heavily on SMBs. Digital acceleration has made them more vulnerable to exploitation than ever. This calls for increased and quicker cybersecurity adoption for SMBs.
North America will continue to be the largest SMB cybersecurity market during the forecast period but total spending will increase quicker in emerging Asia–Pacific. North America, emerging Asia–Pacific, and Western Europe together accounted for 73 percent of SMB spending on cyber security in 2020. We expect these regions to continue to be the main markets for cybersecurity vendors that are targeting SMBs.
However, North America and Western Europe will account for a declining share of SMB spending on cyber-security during the forecast period, while emerging Asia–Pacific’s share is expected to increase from 23 percent in 2020 to 27 percent by 2025.
Emerging Asia–Pacific region includes two of the world’s largest countries in terms of population—China and India—as well as several other large countries such as Indonesia and the Philippines, all of which are increasingly digitalizing their economies. This region represents a significant opportunity for cybersecurity vendors that target SMBs.
Spend by a solution/service category: managed security services will account for 33 percent of SMB cybersecurity spending in 2025, up from 28% in 2020.
Spend by Route to Market: MSPs and SIs will Account for 41 percent of SMB Cyber-Security Spending in 2025, up from 35 percent in 2020
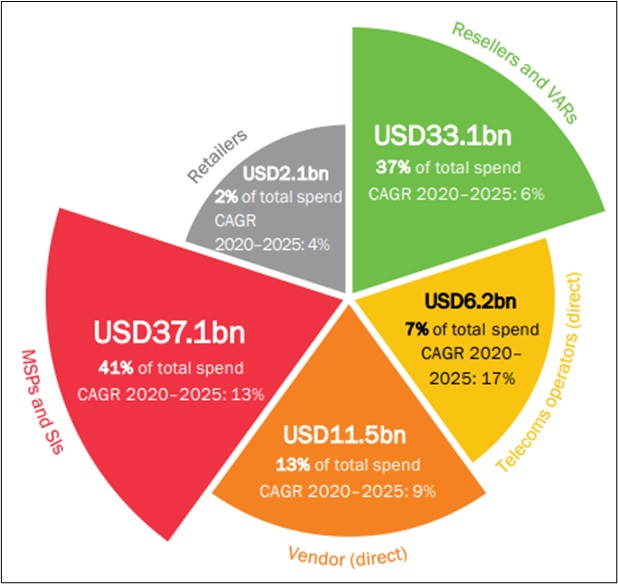
Managed service providers (MSPs) and systems integrators (SIs) were the second-largest route to market for SMB cybersecurity spending worldwide in 2020, behind resellers and value-added resellers (VARs). We expect this to change by 2025 because SMBs will increasingly need managed security services and MSPs/SIs will consequently become more popular partners.
SMB Cybersecurity Spending Worldwide: Forecast Categories
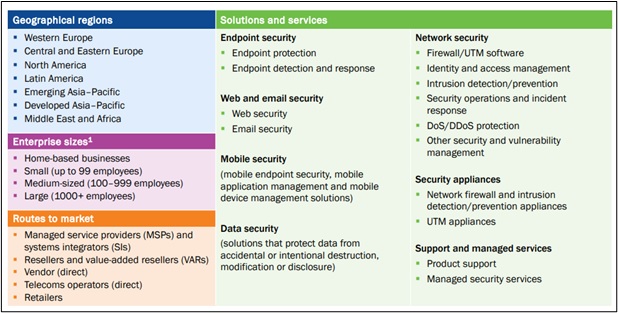
SOC (Security Operations Center) – SANS
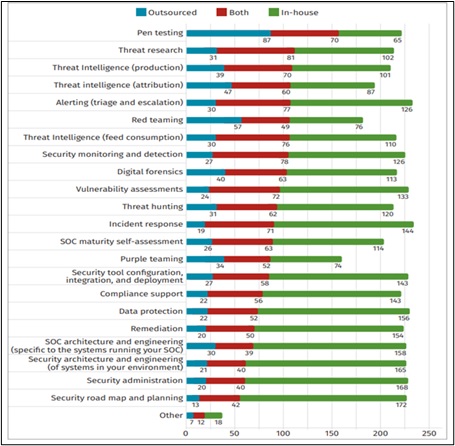
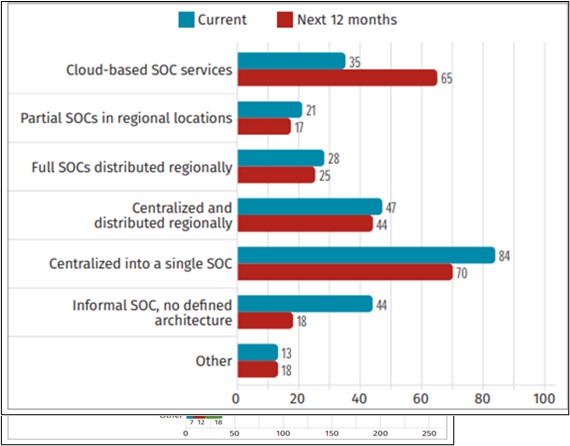
Predictions – Cybersecurity Preparations for 2022
The COVID-19 pandemic is expected to have a significant impact on the way organizations approach security. Aside from this, we also expect to see a major shift in how they hire and store their data. IT and Security should prepare IT systems now to safely and reliably handle an increase in remote workers and the digital fulfillment of market demand.
- Change in Business Model / Increase in online / digitization of sales channel
- Increase in Remote Work
- Increase in Cloud Adoption
- Cost reduction: Resource Optimization /Limited Capex budget
Threats & Vulnerabilities
- Access controls: Lack of Multi-Factor Authentication for remote access
- Social Media and Phishing Attacks
- Ransomware Attacks
- Patch Management: Unpatched Systems connected to network /Unable to Patch on time
- Security Policies and Procedures: No documents or not up to date security Policies & Procedures
- Compliance: Non-Compliance to PCI, HIPAA, GDPR
- People: Skills and Experience



